Detrending time series: Difference between revisions
From Atomix
m Added image |
m Made it a concept |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In the context of analysing turbulence observations, detrending | {{DefineConcept | ||
|description= Detrending typically refers to removing the low-frequency content of the time series | |||
|article_type=Concept | |||
|instrument_type=Velocity point-measurements, Velocity profilers | |||
}} | |||
In the context of analysing turbulence observations, detrending yields a signal that retains mostly contributions from turbulence and surface waves (if present). The resulting detrended signal may contain contributions from frame interference (wakes), vibrations and measurement noise. | |||
Revision as of 17:30, 29 November 2021
| Short definition of Detrending time series |
|---|
| Detrending typically refers to removing the low-frequency content of the time series |
This is the common definition for Detrending time series, but other definitions maybe discussed within the wiki.
{{#default_form:DefineConcept}} {{#arraymap:Velocity point-measurements, Velocity profilers|,|x||}}
In the context of analysing turbulence observations, detrending yields a signal that retains mostly contributions from turbulence and surface waves (if present). The resulting detrended signal may contain contributions from frame interference (wakes), vibrations and measurement noise.
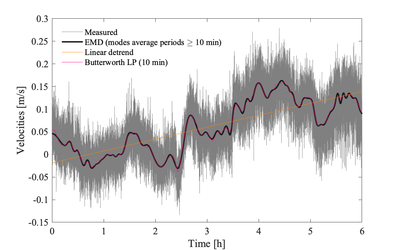
There is no exact definition for what consists of a "trend", nor any set algorithm for identifying the trend [1]. The following techniques can be used for detrending [1]:
- Linear trend removal
- Low-pass filtering using moving averages or linear filters (e.g., butterworth filter)
- Empirical modal decomposition
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 {{#arraymap:Zhaohua Wu, Norden E. Huang, Steven R. Long, and Chung-Kang Peng|,|x|x|, |and}}. 2007. On the trend, detrending, and variability of nonlinear and nonstationary time series. PNAS. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701020104
