Along-beam bin center separation: Difference between revisions
From Atomix
mNo edit summary |
Yuengdjern (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<math>r_0 = z</math> | <math>r_0 = z</math> | ||
where <math>z</math> is the distance from the transducer along the <math>Z</math>-axis. | where <math>z</math> is the distance from the transducer between bin-centers along the <math>Z</math>-axis. | ||
For diverging beams, the along beam bin center separation (<math>r_0</math>) is given by: | For diverging beams, the along beam bin center separation (<math>r_0</math>) is given by: | ||
Revision as of 10:16, 10 December 2021
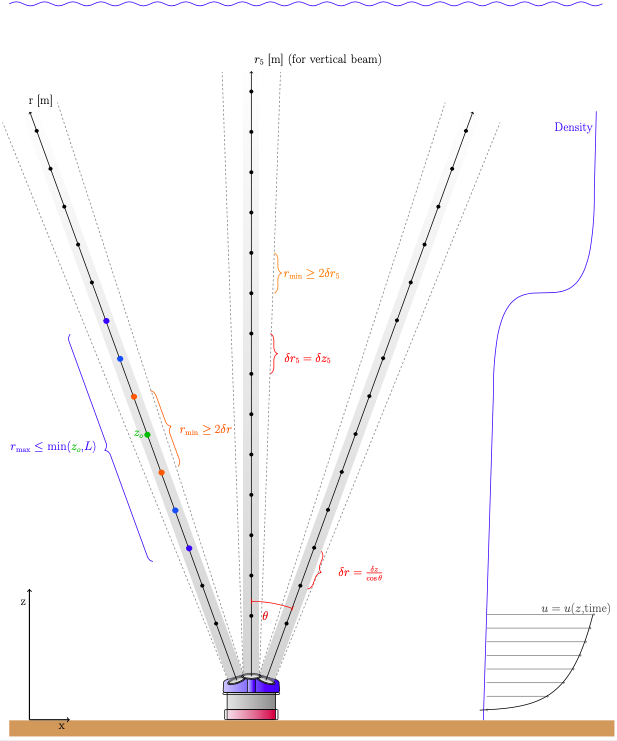
[PLACEHOLDER -- NEED TO CONFIRM THIS IS CORRECT AND/OR ADD PICTURE]
For ADCPs, the -axis in instrument coordinates is commonly defined along the axis of the ADCP pressure case. The velocity data are commonly given in terms of this -coordinate. For a vertical beam, the along beam bin center separation () is given by:
where is the distance from the transducer between bin-centers along the -axis.
For diverging beams, the along beam bin center separation () is given by:
where is the angle of the diverging beams with the -axis.