Along-beam bin center separation: Difference between revisions
Yuengdjern (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Yuengdjern (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
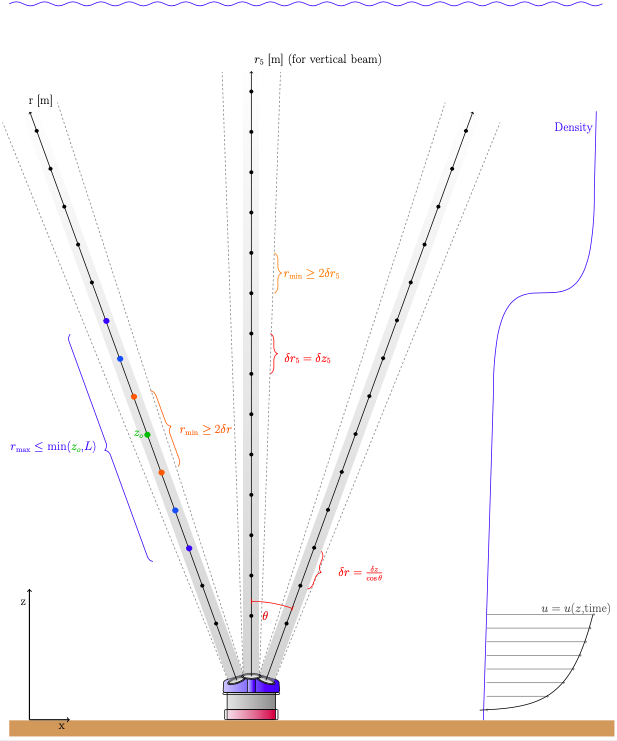
For ADCPs, the <math>Z</math>-axis in instrument coordinates is commonly defined along the axis of the ADCP pressure case. The velocity data are commonly given in terms of this <math>Z</math>-coordinate. For a vertical beam, the along beam bin center separation (<math>r_0</math>) is given by: | For ADCPs, the <math>Z</math>-axis in instrument coordinates is commonly defined along the axis of the ADCP pressure case. The velocity data are commonly given in terms of this <math>Z</math>-coordinate. For a vertical beam, the along beam bin center separation (<math>r_0</math>) is given by: | ||
<math>r_0 = \delta z</math> | <math>\delta r_0 = \delta z</math> | ||
where <math>\delta z</math> is the distance between bin-centers along the <math>Z</math>-axis. | where <math>\delta z</math> is the distance between bin-centers along the <math>Z</math>-axis. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
For diverging beams, the along beam bin center separation (<math>r_0</math>) is given by: | For diverging beams, the along beam bin center separation (<math>r_0</math>) is given by: | ||
<math>r_0 = \frac{\delta z}{\cos\theta}</math> | <math>\delta r_0 = \frac{\delta z}{\cos\theta}</math> | ||
where <math>\theta</math> is the angle of the diverging beams with the <math>Z</math>-axis. | where <math>\theta</math> is the angle of the diverging beams with the <math>Z</math>-axis. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:41, 10 December 2021
For ADCPs, the [math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math]-axis in instrument coordinates is commonly defined along the axis of the ADCP pressure case. The velocity data are commonly given in terms of this [math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math]-coordinate. For a vertical beam, the along beam bin center separation ([math]\displaystyle{ r_0 }[/math]) is given by:
[math]\displaystyle{ \delta r_0 = \delta z }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ \delta z }[/math] is the distance between bin-centers along the [math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math]-axis.
For diverging beams, the along beam bin center separation ([math]\displaystyle{ r_0 }[/math]) is given by:
[math]\displaystyle{ \delta r_0 = \frac{\delta z}{\cos\theta} }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ \theta }[/math] is the angle of the diverging beams with the [math]\displaystyle{ Z }[/math]-axis.
Go back to Compute structure functions and dissipation estimates
