Velocity despiking: Difference between revisions
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|year= 2002|doi= 10.1061/ASCE0733-94292002128:1117}}</ref>. | |year= 2002|doi= 10.1061/ASCE0733-94292002128:1117}}</ref>. | ||
Several techniques exist for | Several techniques exist for despiking. The most used with [[Acoustic-Doppler Velocimeters| acoustic-Doppler velocimeters]] are the phase-space thresholding techniques <ref name="GoringNikora"/>. Other techniques currently being investigated by the subgroup are those used in atmospheric turbulence studies <ref name="Starkenburg">{{Cite journal|authors= D. Starkenburg, S. Metzger, G.J. Fochesatto, J.G Alfieri, R. Gens, A. Prakash and J. Cristobal|journal_or_publisher= J. Atmos. Oceanic Technoly|paper_or_booktitle= Assessment of Despiking Methods for Turbulence Data in Micrometeorology | ||
|year= 2016|doi= 10.1175/JTECH-D-15-0154.1}}</ref>, in particular the median filter despiking technique <ref name="Brock">{{Cite journal|authors=F.V. Brock|journal_or_publisher= J. Atmos. Oceanic Technoly|paper_or_booktitle= A nonlinear filter to remove impulse noise from meteorological data | |year= 2016|doi= 10.1175/JTECH-D-15-0154.1}}</ref>, in particular the median filter despiking technique <ref name="Brock">{{Cite journal|authors=F.V. Brock|journal_or_publisher= J. Atmos. Oceanic Technoly|paper_or_booktitle= A nonlinear filter to remove impulse noise from meteorological data | ||
|year= 1986|doi= 10.1175/1520-0426(1986)003,0051:ANFTRI.2.0.CO;2}}</ref>, which derives its threshold for identifying spurious spikes from the data itself. | |year= 1986|doi= 10.1175/1520-0426(1986)003,0051:ANFTRI.2.0.CO;2}}</ref>, which derives its threshold for identifying spurious spikes from the data itself. | ||
==Filter based methods== | ==Filter based methods== | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 24 November 2021
{{#default_form:Processing}}
{{#arraymap:
Velocity point-measurements
|,|x||}}
{{#arraymap:level 1 raw|,|x||}}
Overview
Any measured signal may be contaminated by spikes. These spikes are typically short-lived and transient, which result in sudden change in the measured signal.
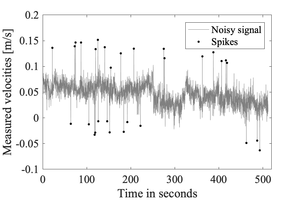
Spikes in velocities measured by acoustic-Doppler velocimeters can result from aliasing of the Doppler signal, in particular when pulses become contaminated by reflecting from complex objects and boundaries [1].
Several techniques exist for despiking. The most used with acoustic-Doppler velocimeters are the phase-space thresholding techniques [1]. Other techniques currently being investigated by the subgroup are those used in atmospheric turbulence studies [2], in particular the median filter despiking technique [3], which derives its threshold for identifying spurious spikes from the data itself.
Filter based methods
Phase-space thresholding methods
Elaborate a bit? Or include information in a separate page
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 {{#arraymap:D. G. Goring and V.I. Nikora|,|x|x|, |and}}. 2002. Despiking Acoustic Doppler Velocimeter Data. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering. doi:10.1061/ASCE0733-94292002128:1117
- ↑ {{#arraymap:D. Starkenburg, S. Metzger, G.J. Fochesatto, J.G Alfieri, R. Gens, A. Prakash and J. Cristobal|,|x|x|, |and}}. 2016. Assessment of Despiking Methods for Turbulence Data in Micrometeorology. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technoly. doi:10.1175/JTECH-D-15-0154.1
- ↑ {{#arraymap:F.V. Brock|,|x|x|, |and}}. 1986. A nonlinear filter to remove impulse noise from meteorological data. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technoly. doi:10.1175/1520-0426(1986)003,0051:ANFTRI.2.0.CO;2
