Processing your ADCP data using structure function techniques
From Atomix
To calculate the dissipation rate at a specific range bin and a specific time ensemble:
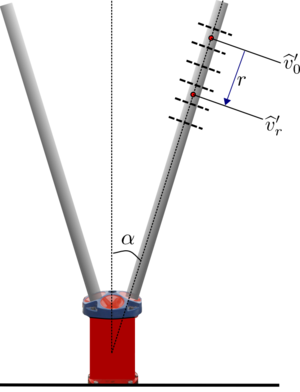
- Extract or compute the along-beam bin center separation [] based on the instrument geometry
- Calculate the along-beam velocity fluctuation time-series in each bin , where [Failed to parse (syntax error): {\displaystyle v’(n, t)} ] from the along-beam velocity data that has met the QC criteria (i.e. the data in Level 2 of the netcdf file)
- Select the maximum distance () over which to compute the structure function based on conditions of the flow (e.g., expected max overturn). The corresponding number of bins is []
- Calculate the structure function for all possible bin separations within using either a bin-centred difference scheme or a forward-difference scheme.
- Perform a regression of against for the appropriate range of bins and r0 separation distances. Be aware of special considerations for forward-difference, center-difference schemes.
- Use the coefficient to calculate as
where is an empirical constant, typically taken as 2.0 or 2.1.
Next step: Apply quality-control on dissipation rates (QA2)
Previous step: Apply quality-control on velocity time series data (QA1)
Return to ADCP Flow Chart front page
