Segmenting datasets
From Atomix
Once the raw observations have been quality-controlled, then you must split the time series into shorter segments by considering:
- Time and length scales of turbulence
- Stationarity of the segment and Taylor's frozen turbulence hypothesis
- Statistical significance of the resulting spectra
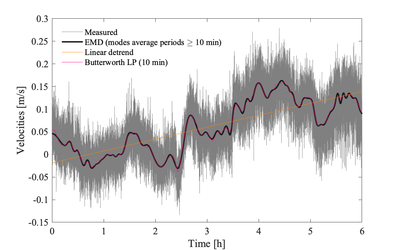
Application to measured velocities
Measurements are typically collected in the following two ways:
- continuously, or in such long bursts that they can be considered continuous
- short bursts that are typically at most 2-3x the expected largest turbulence time scales (e.g., 10 min in ocean environments)
This segmenting step dictates the minimum burst duration when setting up your equipment. The act of chopping a time series into smaller subsets, i.e., segments, is effectively a form of low-pass (box-car) filtering. How to segment the time series is usually a more important consideration than detrending the time series since estimating relies on resolving the inertial subrange in the final spectra computed over each segment.
-
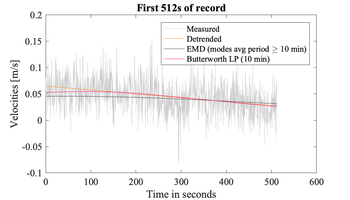
Zoom of the first 512 s segment of the measured velocities shown above including the same trends -
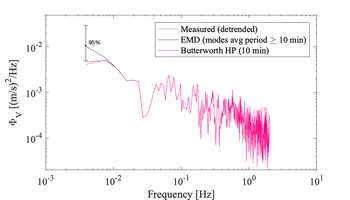
Example velocity spectra of the short 512 s of records before and after different detrending techniques applied to the original 6h time series. The impact of the detrending method can be seen at the lowest frequencies only
Trade-offs when choosing segment length
The shorter the segment, the higher the temporal resolution of the final time series.
Notes
- ↑ {{#arraymap:Zhaohua Wu, Norden E. Huang, Steven R. Long, and Chung-Kang Peng|,|x|x|, |and}}. 2007. On the trend, detrending, and variability of nonlinear and nonstationary time series. PNAS. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701020104
